Introduction: A Country That Moves But Doesn’t Fall
Imagine waking up to your phone buzzing not from a call or message, but a warning. You have just a few seconds to take cover. Somewhere deep beneath the earth, two tectonic plates have shifted, and the ground beneath you is about to shake.
This is not a scene from a movie. This is daily life in Japan, a country that has learned to coexist with earthquakes not with fear, but with preparation, technology, and community resilience.
Japan Earthquake Technology is not just a field of science it’s a way of life, a culture of preparedness and a national promise to protect lives. In a country that faces more than 1,500 earthquakes a year, Japan doesn’t merely endure natural disasters it innovates through them. This is the story of how Japan Earthquake Technology became a symbol of resilience, blending smart engineering, fast communication, and human compassion.
Let’s explore how Japan turned seismic vulnerability into a story of hope, strength, and innovation.
Why Earthquakes Are Part of Japan’s Reality
Japan’s geography is both a blessing and a burden. Its mountains, hot springs, and fertile lands come from powerful geological forces. But those same forces cause devastating earthquakes.
The nation sits where four massive tectonic plates meet—the Pacific, Philippine Sea, Okhotsk and Amur plates. This unique location places Japan squarely on the Pacific Ring of Fire, one of the most seismically active regions on Earth.
The scars are still visible from the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake a magnitude 9.0 disaster that triggered a massive tsunami and nuclear meltdown, leaving behind a trail of heartbreak, resilience and resolve. That day was a turning point in Japan’s long relationship with the Earth’s tremors.
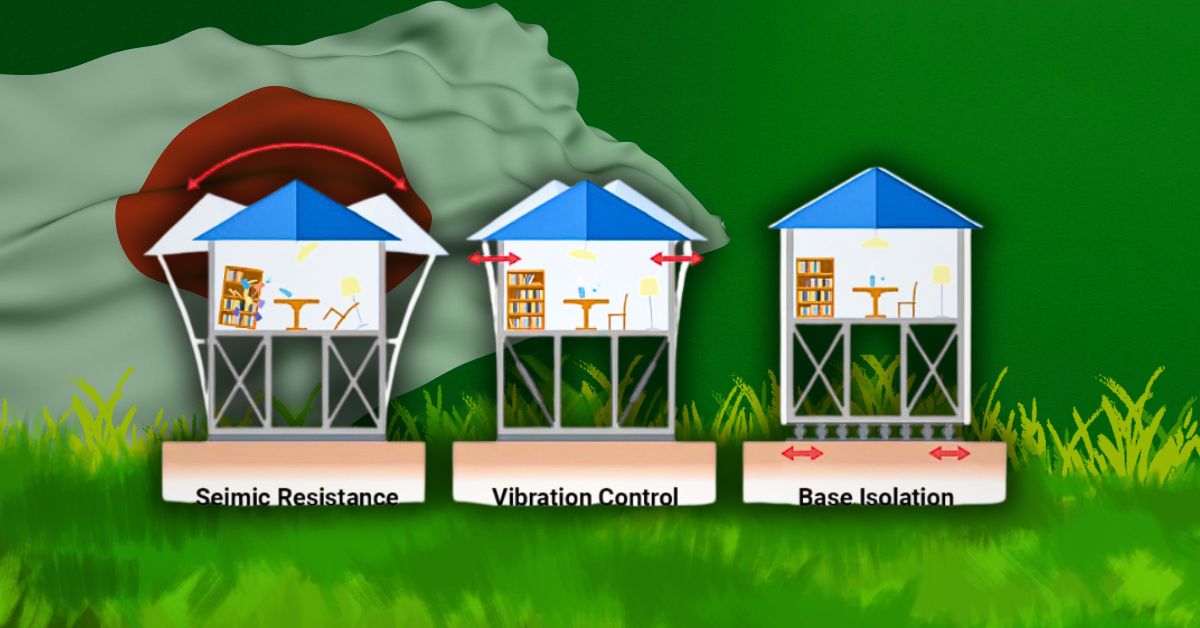
When Buildings Sway Gracefully: Engineering That Saves Lives
In many countries, tall buildings are feared in earthquakes. In Japan, they’re trusted. How? Because Japan builds them differently. These buildings are not made to resist movement they are made to move.
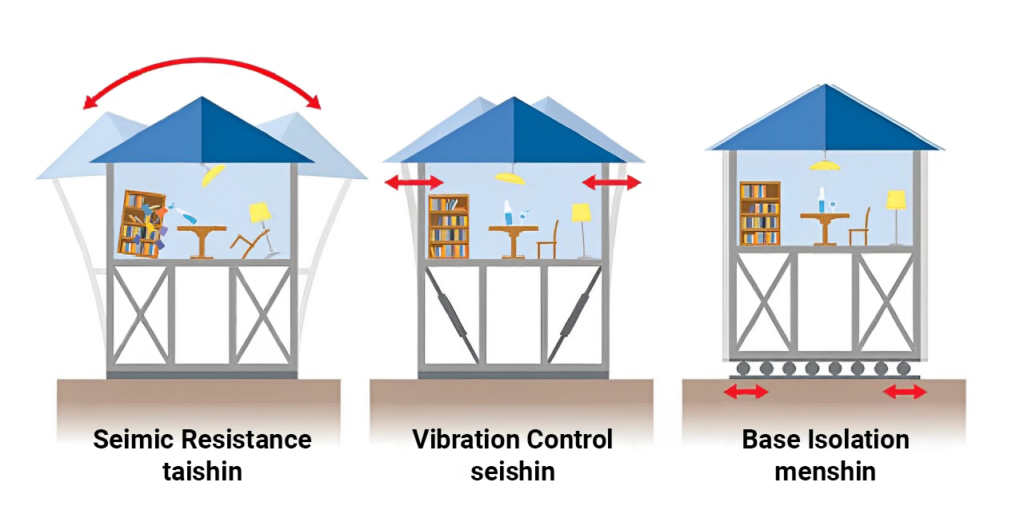
The Magic of Base Isolation
Japan’s engineers know you can’t fight nature, but you can absorb its energy. That’s where base isolation comes in a technique where buildings sit on special rubber or lead pads that allow them to glide slightly during a quake.
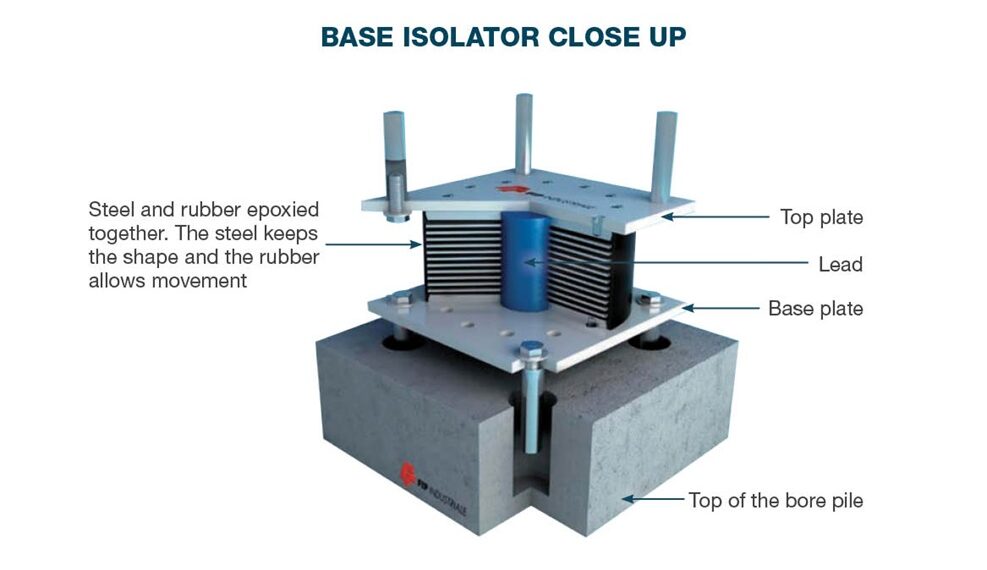
This means when the Earth moves, the building doesn’t jolt violently. It floats, like a ship on waves. Take Tokyo Skytree, for example. It’s the tallest tower in the world. Yet it has a central “spine” that absorbs shock and allows the rest of the structure to sway safely like a tall bamboo in the wind.[Tokyo Skytree Structural Engineering Reports]
Shock Absorbers and Flexible Materials
Some buildings have tuned mass dampers that massive weights that shift during shaking to counterbalance movement. Others are built with steel and treated wood that bend without breaking.
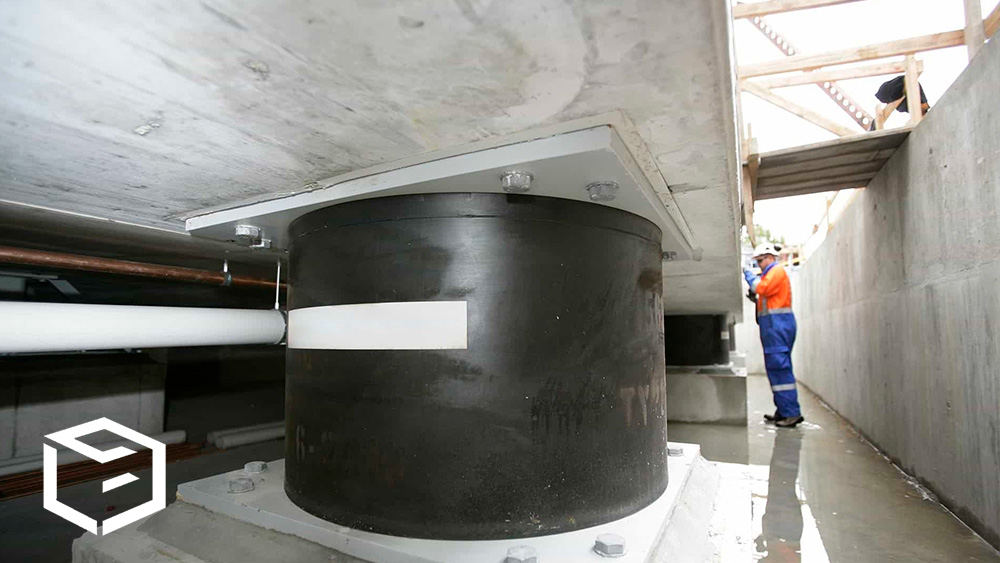

It’s not just about surviving an earthquake only, it’s about walking out afterward and finding the building still standing, safe, and functional.
Seconds That Make a Difference: Japan’s Early Warning System
Imagine you’re on a train, and a warning pops up like “Earthquake detected. Brace for shaking.” The train slows to a stop before you even feel anything. That’s not science fiction. That’s Japan’s Earthquake Early Warning (EEW) system in action.
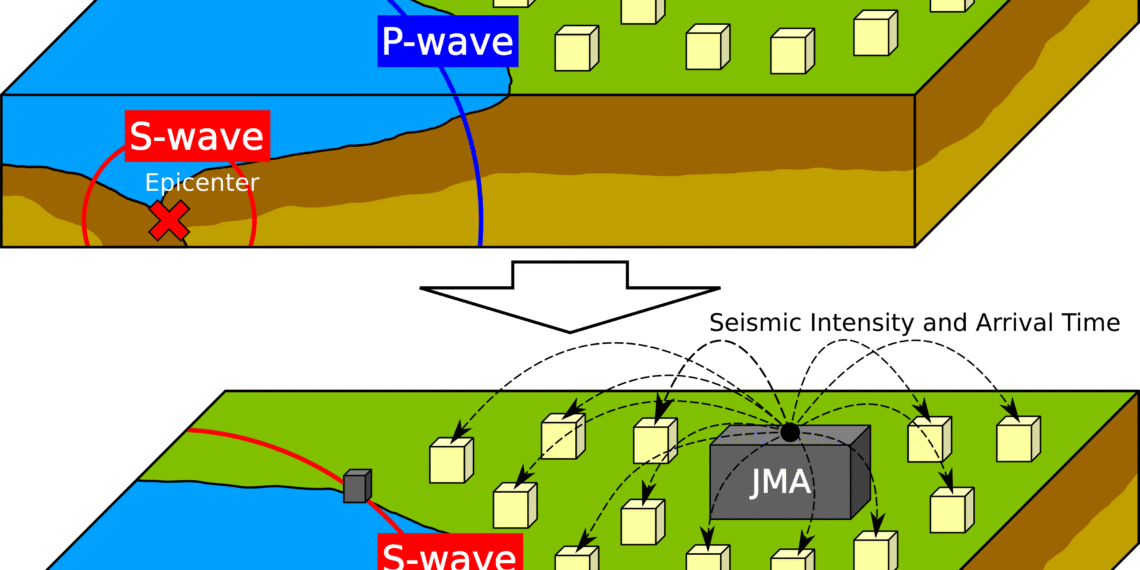
Mechanism of Earthquake Early Warning
How It Works
This incredible system is like a guardian angel made of sensors. Over a thousand seismic stations monitor vibrations across the country. When an earthquake starts, the system detects P-waves- fast, harmless tremors that precede the more destructive S-waves- and sends alerts.
These alerts reach people through:
-
Smartphones
-
TV and radio
-
Public announcement systems
-
School intercoms
-
Factory and train control systems
Sometimes you only get 5–10 seconds of warning but those seconds can be life-saving. You can stop your car, step away from windows, or simply find a safer spot to protect yourself.
Read more: Bus Owners Demand Extra Tk 200 Per Passenger 7 Days Before and After Eid
Stopping Trains, Saving Lives
Perhaps the most incredible feature is how the system can automatically halt bullet trains (Shinkansen). These trains, often traveling over 300 km/h, receive alerts and brake automatically. In 2011, not a single derailment occurred, thanks to this technology. It’s a perfect example of how science, when combined with empathy can protect millions.
Sensors, Satellites, and Smart Buildings: The Role of Smart Infrastructure
Beyond warnings, Japan has wired its cities, buildings, and even the ocean floor with smart tech.
- The GEONET and Fiber Networks(Geospatial Information Authority of Japan (GSI / GEONET)
The GEONET system uses GPS stations to monitor tiny shifts in the Earth’s crust. It detects if land is slowly bending or if a fault is building up pressure with helping predict potential danger zones. Meanwhile, fiber optic cables under bridges, roads, and tunnels act like nerves, sensing stress or damage in real-time.
- AI and Drones After Disaster
Once a quake hits, drones and satellites fly into action. They take images, map destruction, and use AI to calculate which buildings are at risk of collapse. In some hospitals and cities, this data helps emergency crews prioritize rescue missions going first to areas where lives are most in danger.
Not Just Earthquakes also The Tsunami Challenge
If an earthquake happens offshore, there’s another nightmare Japan must face tsunamis. The 2011 tsunami waves reached over 40 meters high in some places, killing thousands and sweeping entire towns into the sea.
- Early Warnings from the Deep
Japan now uses the DART system, which places pressure sensors on the ocean floor. When an underwater quake disturbs the sea, these sensors alert coastal communities within minutes.[NOAA – DART Tsunami Warning System (used by Japan)]
Sirens blare, warnings go out, and families rush to higher ground. It’s a race against time.
- Massive Sea Walls and Escape Plans
In some towns, Japan has built concrete walls as high as buildings, designed to slow down tsunami waves. Coastal roads are lined with evacuation signs, pointing the way to safe towers and hills. It’s not just engineering, it’s the spirit of a country that refuses to give up on protecting its people.
Prepared Citizens the Soul of Earthquake Resilience
Technology means little without people who truly understand how to use it, especially in moments of crisis. That’s why Japan prioritizes education and community readiness as key pillars of its earthquake strategy. From school drills to neighborhood evacuation plans, Japan ensures its citizens are not just informed but empowered to act quickly and calmly.
Drills in Every School
From kindergarten onward to students learn what to do when the earth shakes. They practice hiding under desks, using emergency exits, and helping others. Disaster Prevention Day on September 1st is a national event, with millions taking part in earthquake and tsunami drills. The date marks the anniversary of the 1923 Great Kanto Earthquake, which claimed over 140,000 lives. The memory is painful but the lessons live on.
Emergency Bags and Community Shelters
In most Japanese homes, there’s an emergency bag—a backpack with:
-
Flashlights
-
Dry food and water
-
First aid supplies
-
Phone chargers
-
Warm clothing
Families know where the nearest shelter is, and communities train together to survive together. This shared responsibility is part of what makes Japan’s approach so powerful.
The Aftermath: Recovery with Dignity and Speed
Even the best technology can’t stop all disasters. But Japan has invested deeply in how to recover when the worst happens.
- Drones, Satellites, and Apps
After a quake, authorities use drones to map the damage and apps to let citizens report what they see. This helps emergency crews focus their efforts where they’re needed most.
- Blockchain and Cloud Systems
Hospitals and city halls increasingly use cloud storage and blockchain to keep records safe, even if buildings are destroyed. This protects include-
-
Medical records
-
Insurance policies
-
Identity and ownership documents
These systems helped speed up recovery in places like Kumamoto where a 2016 quake left thousands homeless.
Laws That Save Lives: Government’s Role
None of this works without strong laws and active governance.
- The Building Standard Law
Japan has some of the world’s toughest building codes. After the 1995 Kobe earthquake, millions of buildings were retrofitted. Today, every new building must pass rigorous quake resistance standards.[Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT), Japan]
Research That Never Stops
Japan also funds scientific institutions like:
-
NIED (National Research Institute for Earth Science and Disaster Resilience)
-
The Earthquake Research Institute at the University of Tokyo
These centers constantly improve prediction models, study fault lines, and experiment with new building materials. Innovation never sleeps—because the Earth never does either.
Japan’s resilience is not just for Japan. It’s a gift to the world.
Japan Earthquake Technology : A Market Built on Urgency and Innovation
Japan Earthquake Technology has quietly become a global lifeline. Japan doesn’t just keep its secrets. It shares the country trains engineers and emergency respondents from around the world. As seismic activity continues to threaten millions around the world from Turkey and Nepal to Indonesia, Mexico, and the west coast of the United States are looking to Japan not just for inspiration, but for practical solutions.
Read More: Apple Opens $95 Million Settlement Claims Over Siri Privacy Case
Over the years, Japan has built a global reputation as the leader in earthquake readiness. This leadership didn’t come from textbooks it came from real pain, specially after catastrophic events like the 1995 Kobe earthquake and the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake. These tragedies pushed Japan to develop the world’s most advanced seismic technologies technologies that the world now depends on. Japan’s resilience is not just for Japan. It’s a gift to the world.
Japanese firms and institutions have become international consultants and suppliers in earthquake-prone regions. For example:
-
Nepal has worked with Japanese engineers to upgrade building codes and install early warning systems.
-
Indonesia, one of the most seismically active nations, has received Japanese seismic sensors and training under bilateral cooperation programs.
-
Mexico, after its deadly earthquakes, turned to Japan for knowledge-sharing on community drills and emergency broadcast systems.
-
The United States, particularly California, has collaborated with Japan on smart infrastructure design and fault-line monitoring using satellites and AI.
International demand has turned Japan Earthquake Technology into a soft power tool. Through the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) and various public-private partnerships, Japan offers aid, training programs, and technology transfers, helping countries build resilient systems from the ground up.
In addition to humanitarian efforts, this global demand contributes to Japan’s economy. Seismic technology is now a major export sector, not just in terms of physical devices like base isolators and sensors, but also in consultancy, construction design, and digital monitoring software.
As climate change and urban expansion increase the vulnerability of cities, Japan’s approach to earthquakes is becoming a blueprint for global resilience. Countries no longer see earthquakes as isolated disasters they see them as challenges that need smart, proven responses. And in this field, Japan leads not only by invention, but by example.
A Nation That Stands, Shakes and Stands Again
There is a quiet strength in how Japan lives with earthquakes. It doesn’t deny the danger. It doesn’t panic. It prepares.
From the highest tower to the smallest child, the entire country moves as one during a crisis. It’s a dance between nature and humanity, and Japan leads with grace.
This resilience is this ability to rise, rebuild, and improve after each shock is more than technology. It is a mindset. A cultural promise. A vow to protect life, even when the ground beneath your feet cannot be trusted.
Let us all learn from Japan not only the science but the spirit.